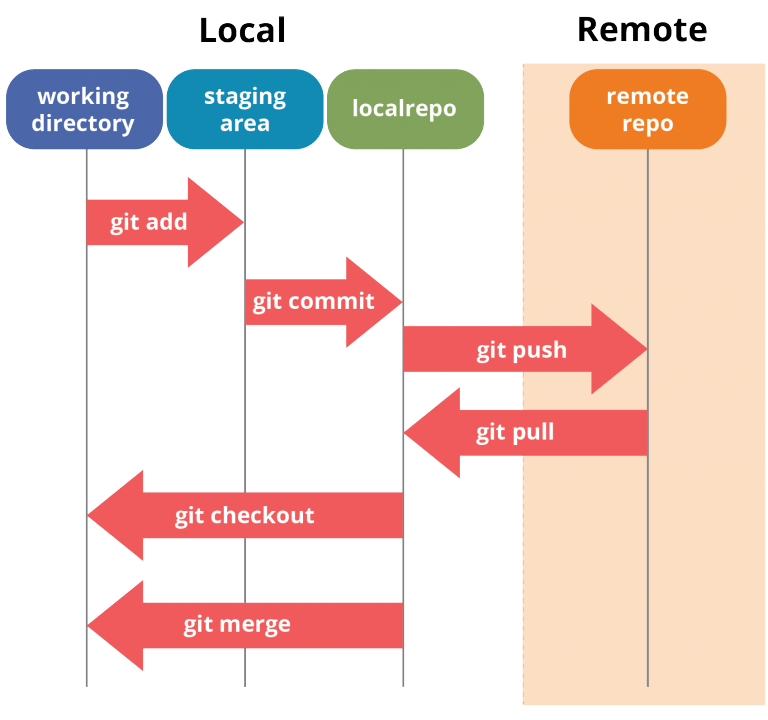
Git Update Repository
Git Update Repository - Web update your local repo from the central repo ( git pull upstream master ). Changing a remote repository's url. The git pull command first runs git fetch which downloads content from the specified remote repository.</p> Watch this video to get a better view on how fetch operation is performed in ide. Web this is a safe way to get an update of all changes to a remote repository. Web if you already have a local repository with a remote url set up for the desired project, you can grab all the new information by using git fetch *remotename* in the terminal:
Make edits, save, git add, and git commit all in your local repo. Web getting started with git / manage remote repositories. Git pull is the most common way to update your repository. Web updating your git repository involves fetching the changes from the remote repository and merging them into your local one. Web if you already have a local repository with a remote url set up for the desired project, you can grab all the new information by using git fetch *remotename* in the terminal:
Select git | fetch in the main menu. Web this is a safe way to get an update of all changes to a remote repository. Changing a remote repository's url. Web updating your git repository involves fetching the changes from the remote repository and merging them into your local one. However, you may want to use git fetch instead.
Web git merge will update your current branch with any new commits on the remote tracking branch. Learn to work with your local repositories on your computer and remote repositories hosted on github. This process is typically performed with the `git pull` command, which is a combination of `git fetch` and `git merge`. Make edits, save, git add, and git.
Alternatively, open the branches popup and click in the upper right corner. Select git | fetch in the main menu. There are two ways to fetch changes from the upstream: Watch this video to get a better view on how fetch operation is performed in ide. This process is typically performed with the `git pull` command, which is a combination.
Else if you want to update a specific branch you can use. Web update your local repo from the central repo ( git pull upstream master ). Push changes from local repo to your fork on github.com ( git push origin master) update the central repo from your fork ( pull request) repeat. Web we'll assume that you want to.
Web to update your local repository with remote repository you can use. Otherwise, you can always add a new remote and then fetch. If you haven't made any changes locally, you can use git pull to bring down any new commits and add them to your master. Else if you want to update a specific branch you can use. Make.
Changing a remote repository's url. However, you may want to use git fetch instead. Web if you already have a local repository with a remote url set up for the desired project, you can grab all the new information by using git fetch *remotename* in the terminal: Web update your local repo from the central repo ( git pull upstream.
Web updating your git repository involves fetching the changes from the remote repository and merging them into your local one. If you haven't made any changes locally, you can use git pull to bring down any new commits and add them to your master. Web to update your local repository with remote repository you can use. Select git | fetch.
If you haven't made any changes locally, you can use git pull to bring down any new commits and add them to your master. Web we'll assume that you want to update your master branch. Learn to work with your local repositories on your computer and remote repositories hosted on github. Web update your local repo from the central repo.
However, you may want to use git fetch instead. If you haven't made any changes locally, you can use git pull to bring down any new commits and add them to your master. Web if you already have a local repository with a remote url set up for the desired project, you can grab all the new information by using.
Push changes from local repo to your fork on github.com ( git push origin master) update the central repo from your fork ( pull request) repeat. Replace with your branch. Web updating your git repository involves fetching the changes from the remote repository and merging them into your local one. Otherwise, you can always add a new remote and then.
Git pull is the most common way to update your repository. Learn to work with your local repositories on your computer and remote repositories hosted on github. The git pull command first runs git fetch which downloads content from the specified remote repository.</p> Web to update your local repository with remote repository you can use. Select git | fetch in.
Git Update Repository - Git pull is the most common way to update your repository. Otherwise, you can always add a new remote and then fetch. One reason to do this may be that you expect conflicts. The git pull command first runs git fetch which downloads content from the specified remote repository.</p> Replace with your branch. Web we'll assume that you want to update your master branch. Web git merge will update your current branch with any new commits on the remote tracking branch. This process is typically performed with the `git pull` command, which is a combination of `git fetch` and `git merge`. There are two ways to fetch changes from the upstream: Web this is a safe way to get an update of all changes to a remote repository.
If you haven't made any changes locally, you can use git pull to bring down any new commits and add them to your master. Select git | fetch in the main menu. Watch this video to get a better view on how fetch operation is performed in ide. Web we'll assume that you want to update your master branch. Web update your local repo from the central repo ( git pull upstream master ).
Push changes from local repo to your fork on github.com ( git push origin master) update the central repo from your fork ( pull request) repeat. This process is typically performed with the `git pull` command, which is a combination of `git fetch` and `git merge`. Web this is a safe way to get an update of all changes to a remote repository. If you haven't made any changes locally, you can use git pull to bring down any new commits and add them to your master.
Changing a remote repository's url. Web git merge will update your current branch with any new commits on the remote tracking branch. There are two ways to fetch changes from the upstream:
Replace with your branch. Watch this video to get a better view on how fetch operation is performed in ide. Web update your local repo from the central repo ( git pull upstream master ).
Web To Add A New Remote Git Repository As A Shortname You Can Reference Easily, Run Git Remote Add :
Alternatively, open the branches popup and click in the upper right corner. Replace with your branch. Push changes from local repo to your fork on github.com ( git push origin master) update the central repo from your fork ( pull request) repeat. Else if you want to update a specific branch you can use.
If You Haven't Made Any Changes Locally, You Can Use Git Pull To Bring Down Any New Commits And Add Them To Your Master.
Web we'll assume that you want to update your master branch. This process is typically performed with the `git pull` command, which is a combination of `git fetch` and `git merge`. Web updating your git repository involves fetching the changes from the remote repository and merging them into your local one. Web this is a safe way to get an update of all changes to a remote repository.
Web Getting Started With Git / Manage Remote Repositories.
Learn to work with your local repositories on your computer and remote repositories hosted on github. Changing a remote repository's url. Web update your local repo from the central repo ( git pull upstream master ). Web git merge will update your current branch with any new commits on the remote tracking branch.
Git Pull Is The Most Common Way To Update Your Repository.
One reason to do this may be that you expect conflicts. However, you may want to use git fetch instead. Web to update your local repository with remote repository you can use. The git pull command first runs git fetch which downloads content from the specified remote repository.</p>