Kingdoms And Domains Chart
Kingdoms And Domains Chart - Plantae, contains all plants on earth. Web the three domains of life (archaea, eubacteria and eukarya) quickly supplanted the older division of living things into five kingdoms, the monera (prokaryotes), protista, fungi, plants, and animals (all eukaryotes!). Animalia, contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms: Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Animal classification is the process of identifying, naming and organizing animal species into groups.
Web what is a domain? The taxonomic classification system uses a hierarchical model to organize living organisms into increasingly specific categories. The fungus kingdom contains 8 phyla. These domains are based primarily on the presence or absence of a nucleus. Humans are part of the animal kingdom taxonomy.
Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. Web the domain is the highest ranking of biological classification at this time* and includes 3 domains: From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. This domain includes prokaryotic organisms (which lack a nucleus) that differ from bacteria in membrane composition and rna. Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone.
Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. Find out more about the animal kingdom at our main animals page. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that.
In other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. Humans are part of the animal kingdom taxonomy. Web all organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life: Web the domain is the highest ranking of biological classification at this time* and includes 3 domains: Web today organisms are grouped into.
Find out more about the animal kingdom at our main animals page. Web animal classification examples chart. These domains are based primarily on the presence or absence of a nucleus. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus.
Find out more about the animal kingdom at our main animals page. Web the three domains of life (archaea, eubacteria and eukarya) quickly supplanted the older division of living things into five kingdoms, the monera (prokaryotes), protista, fungi, plants, and animals (all eukaryotes!). The first domain is bacteria. Web in biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just.
In a final surprise, the sequences of archaebacterial genes clearly indicate a common ancestry of archaea and eukarya. The first domain is bacteria. In addition, domain (proposed by carl woese) is now widely used as a fundamental rank, although it is not mentioned in any of the nomenclature codes, and is a synonym for dominion (latin: Groups organisms according to.
Table 1 identifies the scientists who introduced the kingdoms and the dates the kingdoms were introduced. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). Create a taxonomy, modeled on the linnaean classification system, for a set of common objects, such as motor vehicles, tools, or office supplies. Groups organisms according.
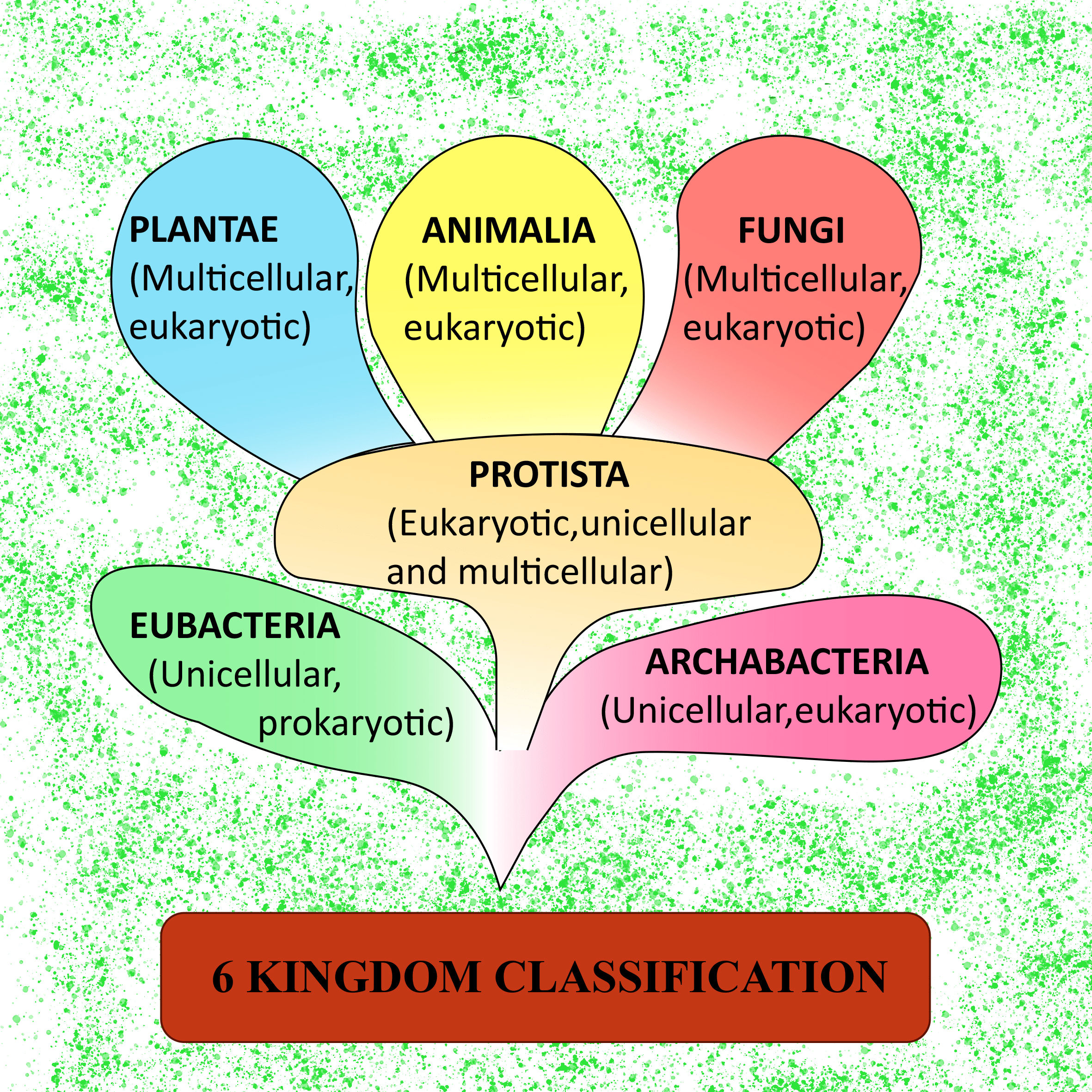
What are the three domains of life on earth? The domains are further subdivided into kingdoms. Dominium), introduced by moore in 1974. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. Table 1 identifies the scientists who introduced the kingdoms and the dates the kingdoms were introduced.
Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, or animalia. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Animal classification is the process of identifying, naming and organizing animal species into groups. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain:
Web the domain is the highest ranking of biological classification at this time* and includes 3 domains: Web animal classification examples chart. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Web the classification system commonly used today is based on the linnean system and has eight levels of taxa; When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria.
Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum..
Kingdoms And Domains Chart - Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: The history of animal classification. Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Web within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Phylum, class, order, family, genus,. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. These domains are based primarily on the presence or absence of a nucleus. Plantae, protozoa, animalia, chromista, and fungi.
Web living organisms can be classified into three domains: There are currently six kingdoms. The history of animal classification. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. What are the three domains of life on earth?
Find out more about the animal kingdom at our main animals page. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum.
After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species.
Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone. Web living organisms can be classified into three domains:
Web For Example, After The Common Beginning Of All Life, Scientists Divide Organisms Into Three Large Categories Called A Domain:
Web the new kingdoms include protista (protists), fungi, monera (eubacteria), and archaea (archaebacteria). They are present in the soil, water, and air. Plantae, protozoa, animalia, chromista, and fungi. Web living organisms can be classified into three domains:
Web Within Each Domain Is A Second Category Called A Kingdom.
This domain includes prokaryotic organisms (which lack a nucleus) that differ from bacteria in membrane composition and rna. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Web the three domains of life (archaea, eubacteria and eukarya) quickly supplanted the older division of living things into five kingdoms, the monera (prokaryotes), protista, fungi, plants, and animals (all eukaryotes!).
Amoebas, Slime Mold, Mildew, Euglena.
Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Create a taxonomy, modeled on the linnaean classification system, for a set of common objects, such as motor vehicles, tools, or office supplies. Humans are part of the animal kingdom taxonomy.
Web What Is A Domain?
The history of animal classification. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, and species. In a final surprise, the sequences of archaebacterial genes clearly indicate a common ancestry of archaea and eukarya.