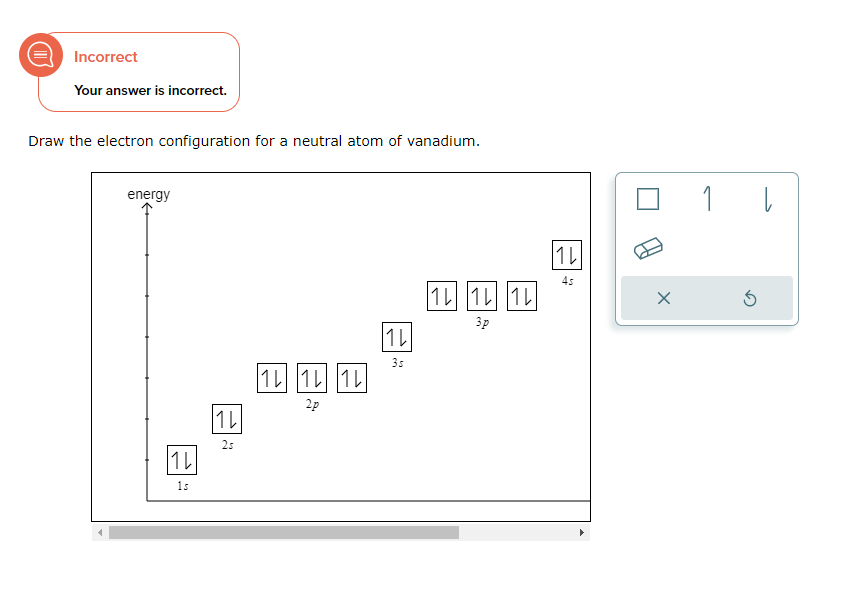
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Zinc
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Zinc - Electron configuration can be done in two ways. Web find the atomic number of nitrogen (7) and use this electron configuration calculator to get a complete electron configuration. The element gallium begins to add electrons to the fourth shell and acts more like aluminum and boron, not cadmium and mercury. Web chemistry questions and answers. What is the name of this atom? An electron configuration shows the distribution of electrons of an atom or a molecule.
The diagram below shows the orbital diagram for a neutral zinc atom in its ground state. Web there are 2 steps to solve this one. Web the electron configuration of zinc is 3d 10 4s 2, if the electron arrangement is through orbitals. This element has 4 energy levels and in its outermost shell it has 2 electrons. Web chemistry questions and answers.
Electron configuration can be done in two ways. This element has 4 energy levels and in its outermost shell it has 2 electrons. Justify the observed charge of ions to their electronic configuration. Web the electron configuration of a neutral zinc atom in its ground state is 1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^63d^104s^2. The diagram below shows the orbital diagram for a neutral zinc atom in its ground state.
The fact that the electron configuration shows that all sublevels are full, indicates that there are no unpaired electrons. Web your solution’s ready to go! The total number of electrons is the atomic number, z. Identify and explain exceptions to predicted electron configurations for atoms and ions. Otherwise, write the order of the energy levels with electron configuration chart:
Web full electron configuration of zinc: Web electron configuration of zinc. A neutral atom has equal numbers of protons and electrons, so a neutral atom of zinc would have 30 electrons. An electron configuration shows the distribution of electrons of an atom or a molecule. 100% (1 rating) share share.
Web there are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species: Justify the observed charge of ions to their electronic configuration. The atomic number of zinc is 30, which means that all zinc atoms have 30 protons in their nuclei. Web to write the configuration for the zinc and the.
Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of zinc. 100% (1 rating) share share. We first need to find the number of electrons for the zn. A neutral atom has equal numbers of protons and electrons, so a neutral atom of zinc would have 30 electrons. Recheck energy try one last time.
The total number of electrons is the atomic number, z. Web there are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species: A neutral atom has equal numbers of protons and electrons, so a neutral atom of zinc would have 30 electrons. Web your solution’s ready to go! Justify the anomalies.
It states that the electrons are filled in an orbital in the increasing order of o. Web full electron configuration of zinc: An atom has a valence shell electron configuration of #ns^1#. The element gallium begins to add electrons to the fourth shell and acts more like aluminum and boron, not cadmium and mercury. Web an electrically neutral atom has.
This indicates that zinc has the same electronic structure as the noble gas argon (ar), followed by two electrons in. Web there are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species: Electron configuration through orbit (bohr principle) electron configuration through orbital (aufbau principle) An atom has a valence shell electron.
Then determine the number of electrons that were lost to form the cation. The shorthand electron configuration (or noble gas configuration) as well as full electron configuration is also mentioned in the table. Web to write the configuration for the zinc and the zinc ion, first we need to write the electron configuration for just zinc (zn). It states that.
The total number of electrons is the atomic number, z. #1s^2, 2 s^2, 2p^6, 3s^2, 3p^4#. View the full answer step 2. Its atomic number is 30, so its complete electron configuration is 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d10 4s2. Web there are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species:
Web the electron configuration of zinc is 3d 10 4s 2, if the electron arrangement is through orbitals. This problem has been solved! The diagram below shows the orbital diagram for a neutral zinc atom in its ground state. What is an electron configuration? Web there are 2 steps to solve this one.
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Zinc - When writing an electron configuration, first write the energy level (the period), then the subshell to be filled and the superscript, which is the number of electrons in that subshell. An atom has a valence shell electron configuration of #ns^1#. Web full electron configuration of zinc: Web your solution’s ready to go! Then determine the number of electrons that were lost to form the cation. This element has 4 energy levels and in its outermost shell it has 2 electrons. This problem has been solved! Web there are 2 steps to solve this one. The diagram below shows the orbital diagram for a neutral zinc atom in its ground state. The fact that the electron configuration shows that all sublevels are full, indicates that there are no unpaired electrons.
Predict the charge of common metallic and nonmetallic elements, and write their electron configurations. To write an electron configuration for a cation, start by writing the electron configuration for the neutral atom. Web an electrically neutral atom has the following electron configuration: What is the name of this atom? We first need to find the number of electrons for the zn.
This problem has been solved! This indicates that zinc has the same electronic structure as the noble gas argon (ar), followed by two electrons in. Its atomic number is 30, so its complete electron configuration is 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d10 4s2. An electron configuration shows the distribution of electrons of an atom or a molecule.
The diagram below shows the orbital diagram for a neutral zinc atom in its ground state. Web the electron configuration of a neutral zinc atom in its ground state is 1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^63d^104s^2. The element gallium begins to add electrons to the fourth shell and acts more like aluminum and boron, not cadmium and mercury.
Web an electrically neutral atom has the following electron configuration: Web chemistry questions and answers. This problem has been solved!
Its Simplified Electron Configuration Is [Ar] 3D¹⁰ 4S².
Web the electron configuration of a neutral zinc atom in its ground state is 1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^63d^104s^2. Web cations are formed when a neutral atom loses electrons. There is a specific notation that can quickly show you where the electrons are likely to be located, so knowing this notation is an essential part of knowing electron configurations. Web electron configuration of zinc.
The Element Gallium Begins To Add Electrons To The Fourth Shell And Acts More Like Aluminum And Boron, Not Cadmium And Mercury.
Web electron configuration chart of all elements is mentioned in the table below. Web full electron configuration of zinc: 100% (1 rating) share share. Predict the charge of common metallic and nonmetallic elements, and write their electron configurations.
Justify The Anomalies Of The Electron Configurations In Transition Metals Using Magnetism Experimental Data.
Electron configuration through orbit (bohr principle) electron configuration through orbital (aufbau principle) Otherwise, write the order of the energy levels with electron configuration chart: The total number of electrons is the atomic number, z. Web there are 2 steps to solve this one.
An Atom Has A Valence Shell Electron Configuration Of #Ns^1#.
Web there are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species: Identify and explain exceptions to predicted electron configurations for atoms and ions. Justify the observed charge of ions to their electronic configuration. Then determine the number of electrons that were lost to form the cation.