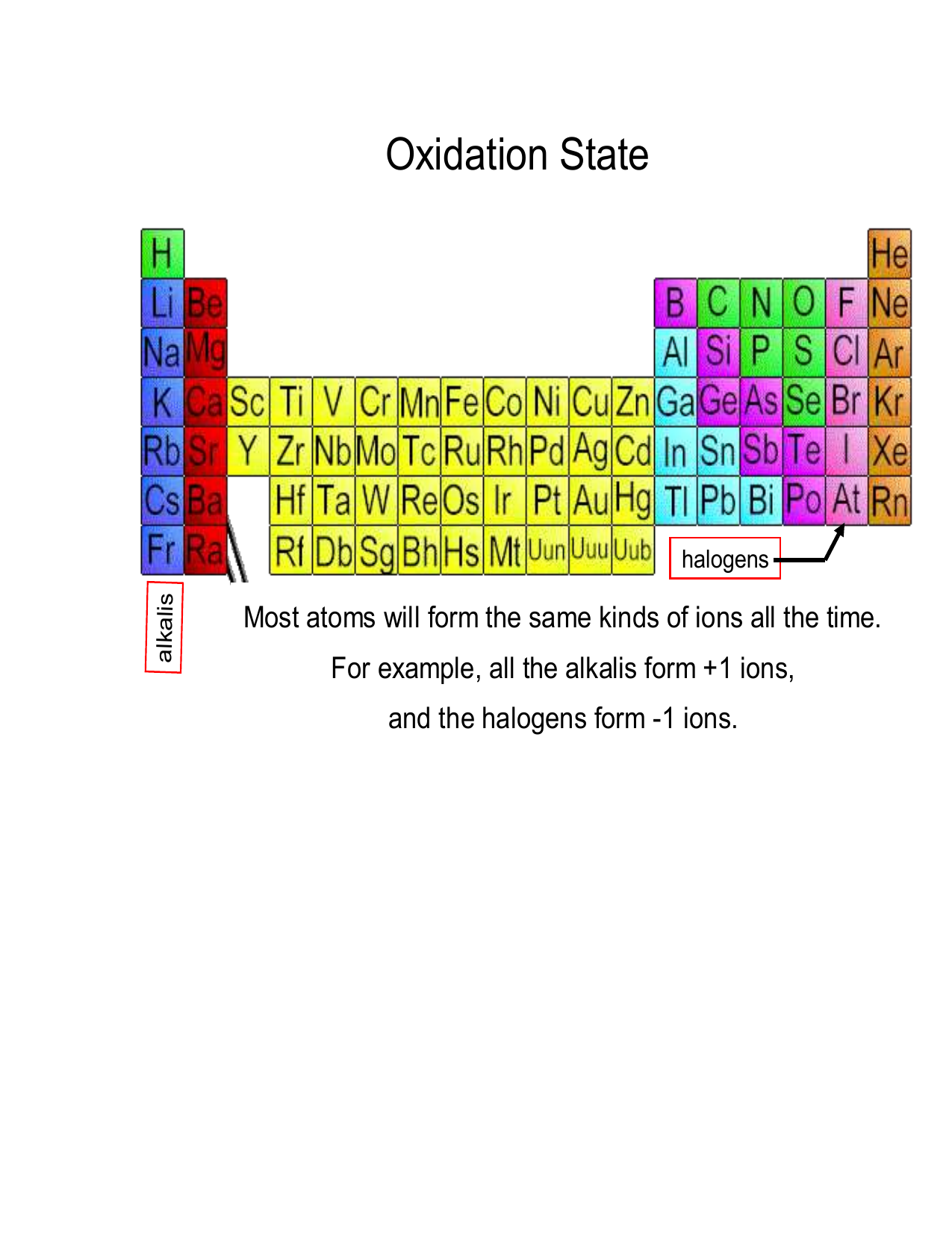
Chart Of Oxidation Number
Chart Of Oxidation Number - Web we can use oxidation numbers to keep track of where electrons are in a molecule, and how they move during a reaction. This table is available for download as a pdf file and printed for offline use. The oxidation number is a positive or negative number that is assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction. The oxidation number of an element or neutral compound is zero. Oxidation number of an atom when an element has combined with the same element It is often useful to follow chemical reactions by looking at changes in the oxidation numbers of the atoms in each compound during the reaction.
Oxidation number of an atom can be positive or negative or may be zero; Mno2 wouldn't be considered an oxyanion because it isn't an anion, it's a neutral compound. Bold numbers represent the more common oxidation states. Otherwise, the total charge is ionic charge. Web the oxidation number represents how many electrons an atom has gained or lost in a molecule.
You can download the chart and the table above by clicking on either. Web what is oxidation number or oxidation state. Web this periodic table contains the oxidation numbers of the elements. Web the oxidation state of an atom is equal to the total number of electrons which have been removed from an element (producing a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (producing a negative oxidation state) to reach its present state. Web the oxidation state of an atom is equal to the total number of electrons which have been removed from an element (producing a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (producing a negative oxidation state) to reach its present state.
A lithium atom has one outer shell electron. Web the oxidation state of an atom is equal to the total number of electrons which have been removed from an element (producing a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (producing a negative oxidation state) to reach its present state. The oxidation number is the positive or negative number of.
The oxidation state tells how many valence electrons an atom accepts (negative number) or donates (positive number) to form a chemical bond. Web enter the formula of a chemical compound to find the oxidation number of each element. Web list of oxidation states of the elements. Redox reactions are characterized by a transfer of electrons. A net ionic charge can.
More than one oxidation numbers of an element; Web list of oxidation states of the elements. Mno2 wouldn't be considered an oxyanion because it isn't an anion, it's a neutral compound. Web enter the formula of a chemical compound to find the oxidation number of each element. Web information of oxidation numbers of monoatomic ions in periodic table.
If you're working out the oxidation states of the atoms in a reaction and you get one that's not on this chart, it's probably worth checking your work. Elements have an oxidation state of zero, and atoms in ionic compounds are usually assigned a positive or negative oxidation state. Web enter the formula of a chemical compound to find the.
Web list of oxidation states of the elements. If you're working out the oxidation states of the atoms in a reaction and you get one that's not on this chart, it's probably worth checking your work. Web table of oxidation states of the elements. The oxidation state tells how many valence electrons an atom accepts (negative number) or donates (positive.
Otherwise, the total charge is ionic charge. In our water example, hydrogen is assigned an oxidation number of +1 because each. Web the oxidation number represents how many electrons an atom has gained or lost in a molecule. The oxidation number is a positive or negative number that is assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or.
The oxidation state tells how many valence electrons an atom accepts (negative number) or donates (positive number) to form a chemical bond. To keep track of electrons in a redox reaction, oxidation numbers are used. Oxidation number of an atom can be positive or negative or may be zero; Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the systematic nomenclature.
The oxidation number is a positive or negative number that is assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction. If you're working out the oxidation states of the atoms in a reaction and you get one that's not on this chart, it's probably worth checking your work. To keep track of electrons in a redox reaction,.
Web an oxidation number is a positive or negative number that is assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction. Web oxidation number, the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom. Web enter the formula of a chemical compound to find the.
Web the corrected table can be found here. The most common oxidation states are in bold. Bold numbers represent the more common oxidation states. Web determine what is the oxidizing and reducing agents in the following reaction. More than one oxidation numbers of an element;
Chart Of Oxidation Number - Web the chart below should help you to visualize the possible oxidation numbers that can occur for the first 39 atoms. Web the oxidation state of an atom is equal to the total number of electrons which have been removed from an element (producing a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (producing a negative oxidation state) to reach its present state. Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the systematic nomenclature of. In our water example, hydrogen is assigned an oxidation number of +1 because each. Web we can use oxidation numbers to keep track of where electrons are in a molecule, and how they move during a reaction. A lithium atom has one outer shell electron. Web list of oxidation states of the elements. Web an oxidation number is a positive or negative number that is assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction. Web this periodic table contains the oxidation numbers of the elements. The oxidation number is the positive or negative number of an atom that indicates the electrical charge the atom has if its compound consists of ions.
Mno2 wouldn't be considered an oxyanion because it isn't an anion, it's a neutral compound. Web determine what is the oxidizing and reducing agents in the following reaction. The most common oxidation states are in bold text and predicted or unconfirmed states are in italics. Web information of oxidation numbers of monoatomic ions in periodic table. Web we can use oxidation numbers to keep track of where electrons are in a molecule, and how they move during a reaction.
Web oxidation number, the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom. Web determine what is the oxidizing and reducing agents in the following reaction. Web we can use oxidation numbers to keep track of where electrons are in a molecule, and how they move during a reaction. Web this periodic table contains the oxidation numbers of the elements.
In our water example, hydrogen is assigned an oxidation number of +1 because each. The most common oxidation states are in bold text and predicted or unconfirmed states are in italics. Elements have an oxidation state of zero, and atoms in ionic compounds are usually assigned a positive or negative oxidation state.
Elements have an oxidation state of zero, and atoms in ionic compounds are usually assigned a positive or negative oxidation state. Web we can use oxidation numbers to keep track of where electrons are in a molecule, and how they move during a reaction. Web an oxidation number is a positive or negative number that is assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction.
Oxidation Number Of An Atom Can Be Positive Or Negative Or May Be Zero;
The atoms in na, o 2, n 2, pb, he, h 2, ne, zn, for example, have oxidation numbers of 0. Web the oxidation number represents how many electrons an atom has gained or lost in a molecule. The oxidation number is also called as the oxidation state. Web the chart below should help you to visualize the possible oxidation numbers that can occur for the first 39 atoms.
Web Oxidation State Shows The Total Number Of Electrons Which Have Been Removed From An Element (A Positive Oxidation State) Or Added To An Element (A Negative Oxidation State) To Get To Its Present State.
Rules for assigning oxidation numbers: To keep track of electrons in a redox reaction, oxidation numbers are used. A lithium atom has one outer shell electron. Enter just an element symbol to show the common and uncommon oxidation states of the element.
Web The Corrected Table Can Be Found Here.
Web enter the formula of a chemical compound to find the oxidation number of each element. Learn how to determine oxidation numbers, along with examples, a diagram, and a chart. This table is available for download as a pdf file and printed for offline use. Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the systematic nomenclature of.
More Than One Oxidation Numbers Of An Element;
Zn + 2h+ zn2+ +h2 zn + 2 h + zn 2 + + h 2. Elements have an oxidation state of zero, and atoms in ionic compounds are usually assigned a positive or negative oxidation state. This table is based on greenwood's,[1] with all additions noted. It is often useful to follow chemical reactions by looking at changes in the oxidation numbers of the atoms in each compound during the reaction.